US Fiscal Dominance Causes
Like navigating a maze, understanding the US economy can be challenging, especially when terms like 'fiscal dominance' come into play.
Fiscal Dominance is a situation where debt and deficit are so high that monetary policy, directed by central banks, can't control inflation effectively. To gain a better understanding of fiscal dominance and it effect on the resurgence of inflation, we must cover the following points:
- What is Fiscal Dominance
- Brands of Fiscal Dominance
- Fiscal Dominance Concerns
- Fiscal Dominance Causes
What causes this? In the modern context, high-interest rates, deficit-driven fiscal stimulus, and a post-COVID economy are all contributing factors. Imagine the fiscal policy as a heavyweight boxer knocking out the monetary policy in the ring.
This article will help you understand the causes of US fiscal dominance, arming you with the knowledge to make sense of economic trends and make informed decisions.
Let's delve into this complex world together.
What is Fiscal Dominance?
Often, you may hear the term 'fiscal dominance' but understanding what it truly means can be a bit complex. It's a condition that arises when a country's debt and deficit levels are so high that traditional monetary policy becomes ineffective in controlling inflation. Interestingly, this isn't due to a failure of monetary policy but rather to an overwhelming fiscal presence.
Consider the process of money creation. Two key drivers are the expansion of bank credit and monetized fiscal deficits. The former involves new money being lent into existence through fractional-reserve banking. The latter involves printing money to fund government spending. When fiscal deficits dominate, the usual tactics of higher policy rates to curb bank credit, and therefore inflation, become ineffective. Here's why: Higher policy rates do limit bank credit, but they also increase debt service costs. This rise in costs leads to larger government deficits and a need for more inflationary printing.
It's a bit of a catch-22. If the source of inflation is deficit-driven, higher interest rates won't solve the problem. They'll actually exacerbate it. So, in an environment of fiscal dominance, traditional monetary policy loses its strength. The data shows this clearly; in countries where government debt exceeds 100% of GDP, the effectiveness of monetary policy is notably degraded. For context, the US debt-to-GDP ratio currently stands at 119%.
In simple terms, fiscal dominance means that the fiscal situation has taken the driver's seat, reducing the power and influence of monetary policy. It's a complex, yet crucial, concept to understand in today's economic landscape.
Brands of Fiscal Dominance
You're now familiar with the concept of fiscal dominance. It's time to broaden your understanding by exploring its different brands - Unwitting Dominance, Insidious Dominance, and Political Dominance.
Each brand offers unique insights into how fiscal dominance manifests and influences economies, highlighting the complexity and multifaceted nature of this phenomenon.
Unwitting Fiscal Dominance
You may not realize it, but several countries have inadvertently fallen into a trap of fiscal dominance, a phenomenon known as 'unwitting dominance.' This situation arises when a nation's fiscal policy becomes dominant over monetary policy, often due to high debt levels.
- Notably, countries in the European Union agreed to a 'fiscal compact' in 2012, which pushed for balanced budgets, inadvertently leading to a clash between monetary and fiscal policies.
- The Swiss, as another example, ran constant surpluses, despite being far below their inflation target for a decade.
- The fiscal contraction in the Eurozone, coupled with falling interest payments on debt, undermined efforts to raise inflation.
- Many countries, post-financial crisis, announced contractionary plans, which clashed with central banks' efforts to target inflation.
- These examples highlight how fiscal dominance can unknowingly emerge, challenging the efficacy of monetary policy.
Insidious Fiscal Dominance
In dealing with fiscal dominance, you might encounter a particularly subtle and harmful type known as 'insidious dominance'. This form of fiscal dominance is characterized by its stealthy onset, resulting from slowly evolving demographics and an increasing burden on social support systems.
The aging global population, with a growing ratio of retirees to workers, is pushing economies toward their fiscal limits. Over time, this leads to increased inflation expectations, diverting resources away from productive uses.
The uncertainty surrounding policy responses to these demographic and fiscal realities creates further strain. Questions about the sustainability of social security and healthcare, potential tax hikes, and the impact on public services contribute to this insidious form of fiscal dominance.
Political Fiscal Dominance
Another significant form of fiscal dominance you need to consider is political dominance, which can often overshadow monetary policy decisions. Political acts that undermine the safety of public debt create a special class of fiscal dominance that simultaneously threatens both inflation and financial stability, forcing the Federal Reserve to prioritize its legislated mandates.
- The value of US Treasuries heavily depends on faith in the government's commitment to maintain policies supporting their value.
- The refusal to raise the debt limit risks eroding this faith, destabilizing financial markets.
- Even a remote possibility of default due to political decisions can cause prudent investors to alter their strategies.
- The political dominance can contribute to higher risk in the financial markets.
- This form of fiscal dominance is a strong influencer of monetary policy decisions, often dictating the direction of interest rates.
Fiscal Dominance Concerns
Data shows that the U.S. debt-to-GDP ratio currently stands at 119%. This level of debt significantly undermines the effectiveness of monetary policies, leading to persistently high inflation rates. The fiscal deficit remains high even with low unemployment, suggesting a troubling economic landscape dominated by fiscal policy.
The COVID-19 pandemic was marked by aggressive fiscal spending, with governments providing substantial relief to families. While this was a necessary response to the crisis, it resulted in a surge of liquidity in the market. This, coupled with low interest rates, ignited inflation pressures.
As an investor, these conditions present a challenging environment. Traditional safe assets like Treasury bonds might lose appeal due to fiscal dominance and the threat of financial repression. Instead, investing in real assets like real estate, commodities, and commodity producers, or diversifying equity holdings internationally may provide some protection against inflation.
Ultimately, your financial stability hinges not only on the Federal Reserve's actions but also on Congress's willingness to tighten fiscal policy. To safeguard your financial future, it's crucial to adapt to fiscal dominance, reassess your portfolio, and consider alternative investment strategies such as precious metals which are immune to debt-fueled inflation.
Benefits of Working with a Reputable Gold Investment Company
When starting on the path of gold investing, working with a credible and trustworthy precious metals vendor is key. Finding an established gold investment company that understands the many vacillations of the gold markets and the numerous variables affecting its price will save much time and hassle. Working with a reputable company with institutional knowledge can assist you with logical price entry points, positioning, and dollar-cost-averaging so you can maximize your investment capital.
Gold IRAs provide additional advantages to merely buying gold from a local dealer. Furthermore, these companies can provide serious gold investors access to competitive prices, transparency, a sound buyback policy, reliable customer service, and robust security protection of their precious metal investments.
Choosing the right gold IRA company will depend on one's unique investing needs. Depending on whether you are a high-net investor looking for the most competitive prices or require a lower investment minimum and affordable entry to the gold market, we have researched and reviewed our best 4 gold IRA and precious metal investment companies that meet those individual needs. In addition to a gold IRA, owning the physical gold in your place of residence is also an option. We have provided links to these companies at the bottom of this article for your convenience.
Tap the banner below to visit Augusta Precious Metals to receive their gold IRA checklist
Fiscal Dominance Causes
As we pivot to the causes of fiscal dominance, you need to consider episodes of such dominance, the looming debt issues, and the risk of inflation.
Historical data shows that high debt and deficit levels can lead to fiscal dominance, rendering monetary policy ineffective in controlling inflation.
It's also crucial to understand that this state of affairs may increase inflation risks, thereby affecting economic stability.
Episodes of Fiscal Dominance
You've seen several episodes of fiscal dominance in the history of the US, with key causes ranging from wartime demands to political pressures for low-interest rates and economic expansion.
- During World War II, the Fed monetized a large share of US debt, prioritizing government funding over inflation control.
- In the 1960s and early 1970s, the Fed funded fiscal deficits through easy monetary policies, leading to inflation.
- The Johnson and Nixon administrations pressured the Fed to keep rates low and stimulate economic expansion.
- The Great Recession saw the Fed stretch its powers with emergency lending programs and bailouts.
- The pandemic has increased US debt dramatically, with political pressure to keep rates low and monetize the debt.
Understanding these episodes helps in predicting future fiscal dominance scenarios.
Looming Debt Issues
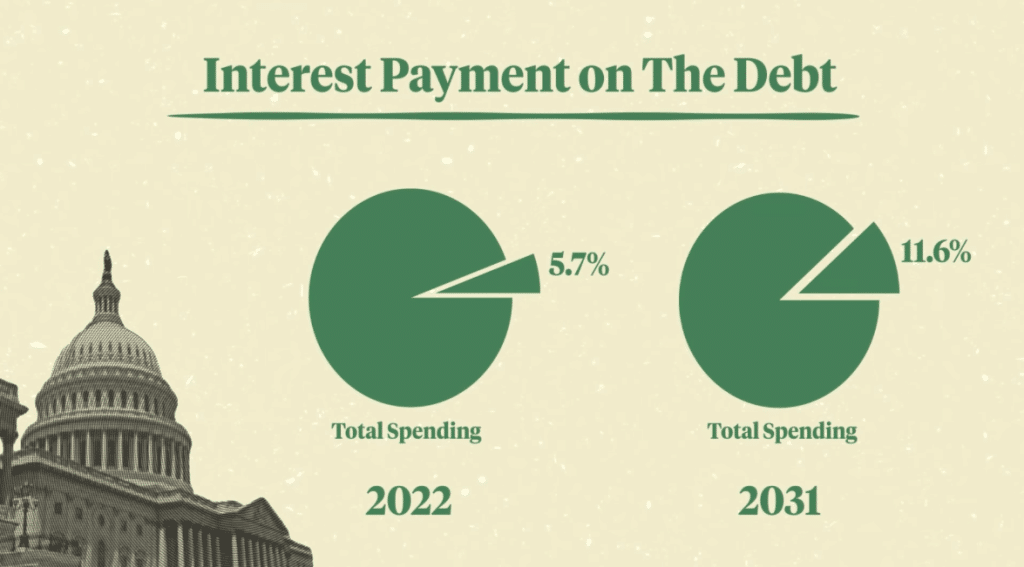
With over 100% of your GDP tied up in debt, the US is facing a looming debt crisis that's a major cause of fiscal dominance. The ratio of US debt to GDP, which was 72% in 2007, has now exceeded 100% and is projected to hit 116% by 2030. This rise is a result of consistent fiscal deficits, as shown in Figure 1.
This situation is further exacerbated by the Federal Reserve's monetization of new debt, causing a spike in money growth. However, inflation remains subdued due to a decline in monetary velocity. Despite these warning signs, some Fed officials remain complacent about the threat of fiscal dominance, increasing the risk of a serious fiscal adjustment in the future.
Risk of Inflation
You're facing a significant risk of inflation due to fiscal dominance, especially as the U.S. debt continues to swell. The Federal Reserve's decision to adopt a flexible average inflation targeting approach, paired with the Biden administration's pressure to keep rates low, could exacerbate this risk.
Factors influencing this inflationary risk include:
- The Fed's willingness to allow annual inflation to exceed 2 percent
- The uncertainty of the time frame for adherence to average inflation of 2 percent
- The potential for market interest rates to increase ahead of the Fed's policy rate target
- The increasing demand for funds as the government floats more debt
- The evolution of inflation expectations impacting investor behavior and bond yields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the causes of US fiscal dominance are complex, intertwined with factors like high interest rates and deficit-driven fiscal stimulus. Understanding these causes is crucial in interpreting our economic trajectory.
Remember, it's not just about the numbers, but the story they tell about our economy's health. Stay informed, stay analytical, and let data drive your understanding of fiscal dominance and its impact on our nation's economic stability.
If you have 100k in savings to protect and want to take advantage of the best prices, attend a gold educational webinar hosted by Augusta Precious Metals. Tap the button below:
Find the right company for you. Obtain a gold IRA guide and talk to a broker




Gold IRA FAQs

Adam ONeill
Author, lifelong investor, and creator of PreciousMetalsInvestmentPortfolio.com